Dead Space In Respiratory System
Dead space in respiratory system. The dead space in that portion of the respiratory system which is external to the alveoli and includes the air-conveying ducts from the nostrils to the terminal bronchioles compare physiological dead space. Dead space is the fraction of tidal volume which does not participate in gas exchange. This ratio increases with age but decreases on exercise.
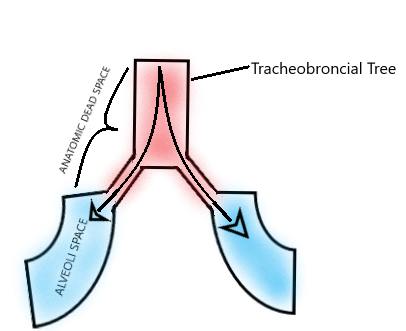
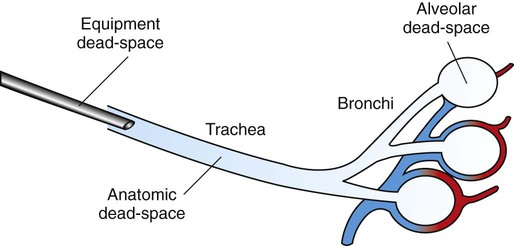
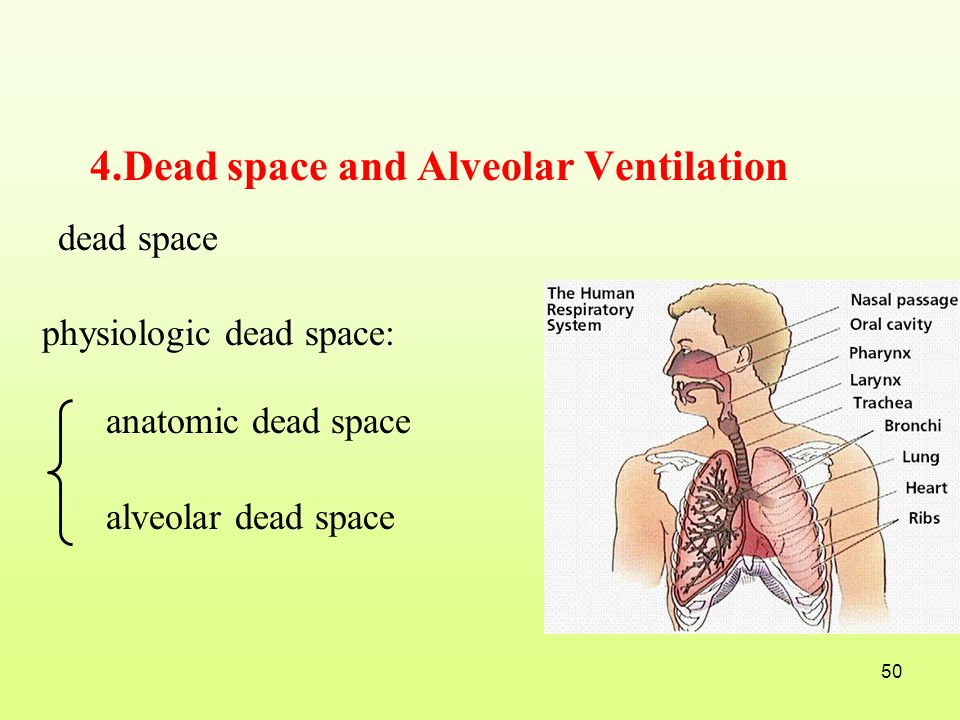
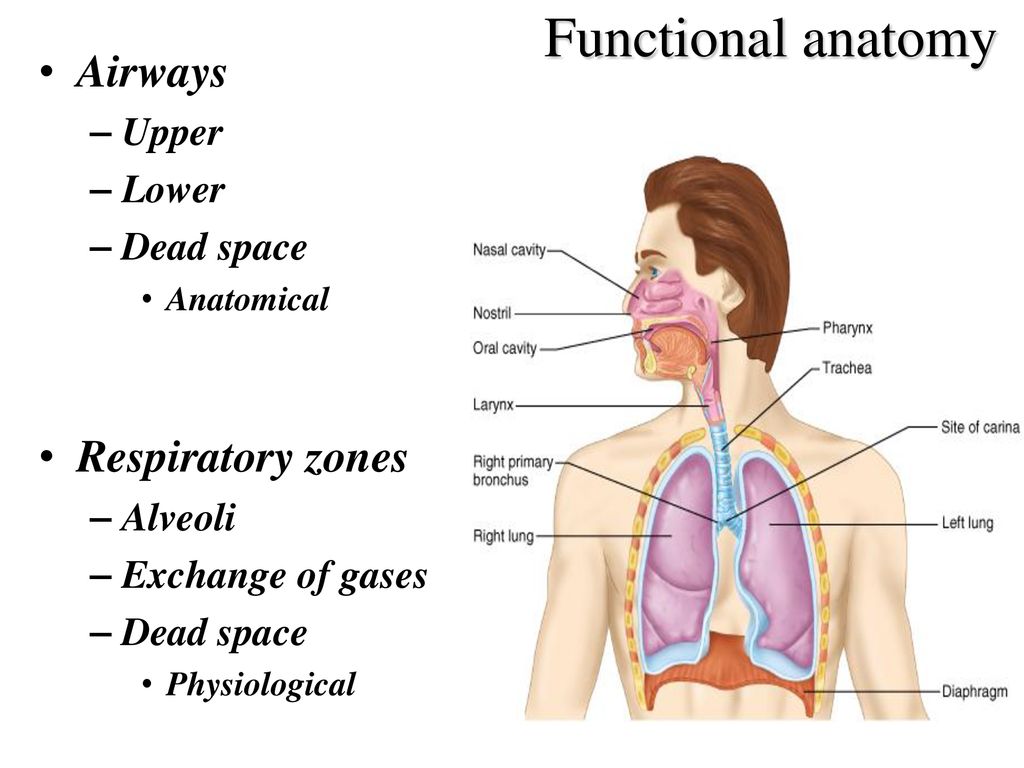
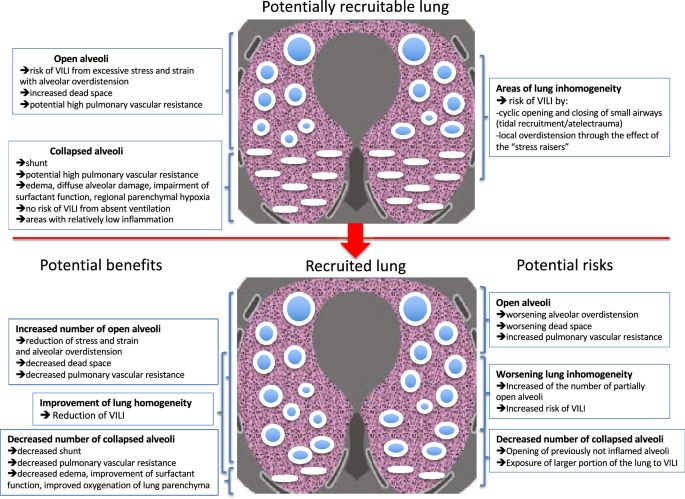
A nonspecific term that fails to distinguish between anatomic dead space and physiologic dead space. Anatomical dead space Vd aw that is the part of airways that do not contribute to gas exchange nose pharynx conduction airways and ventilator equipment if mechanical ventilation is present and alveolar dead space Vd alv or alveoli which are well-ventilated but poorly perfused 12. No matter what we do we cannot ever use this air for gas exchange.
Bronchi arre smaller and lung volumes are smaller low airway resistance. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. VT is similar to adult.
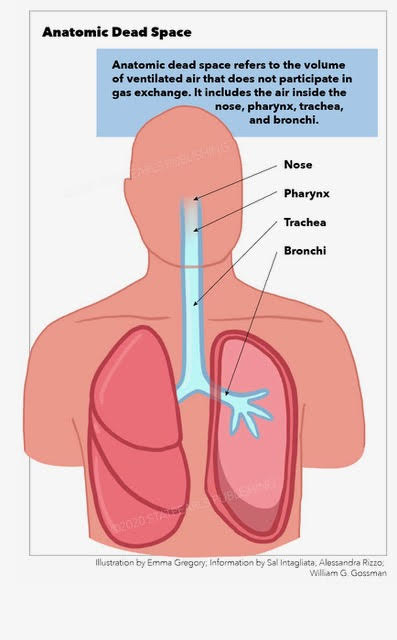
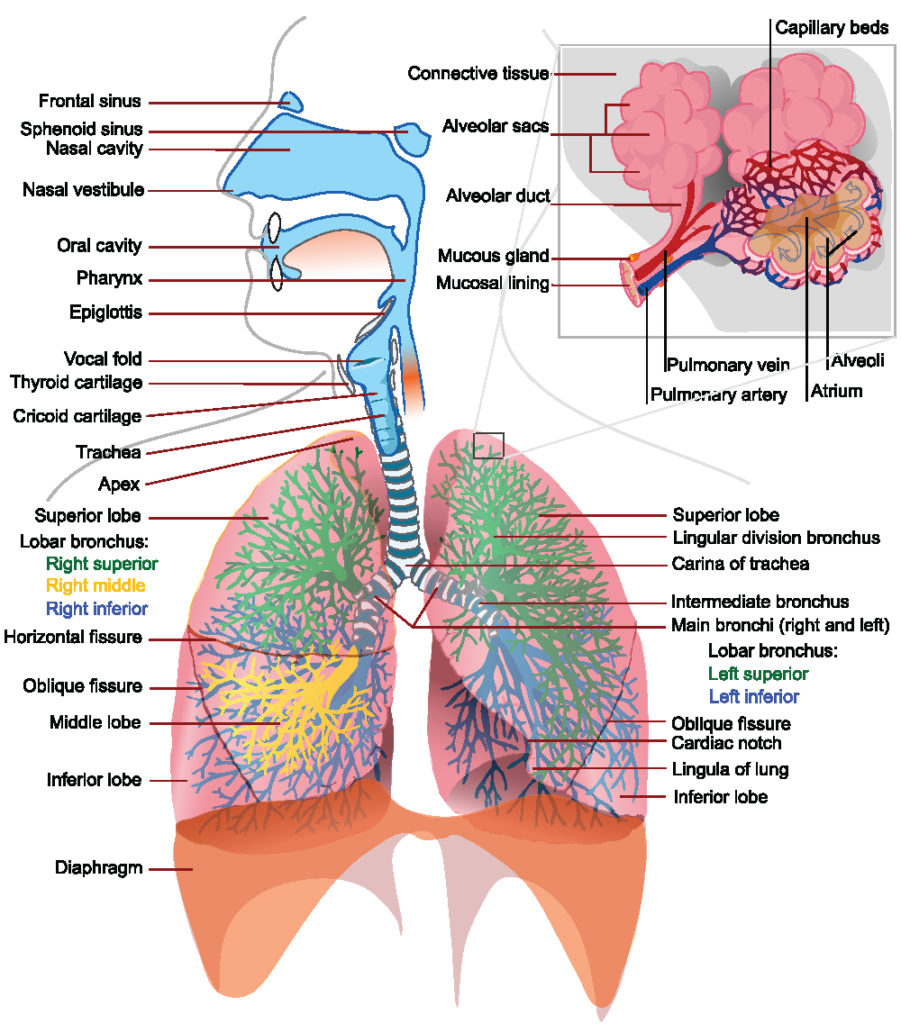
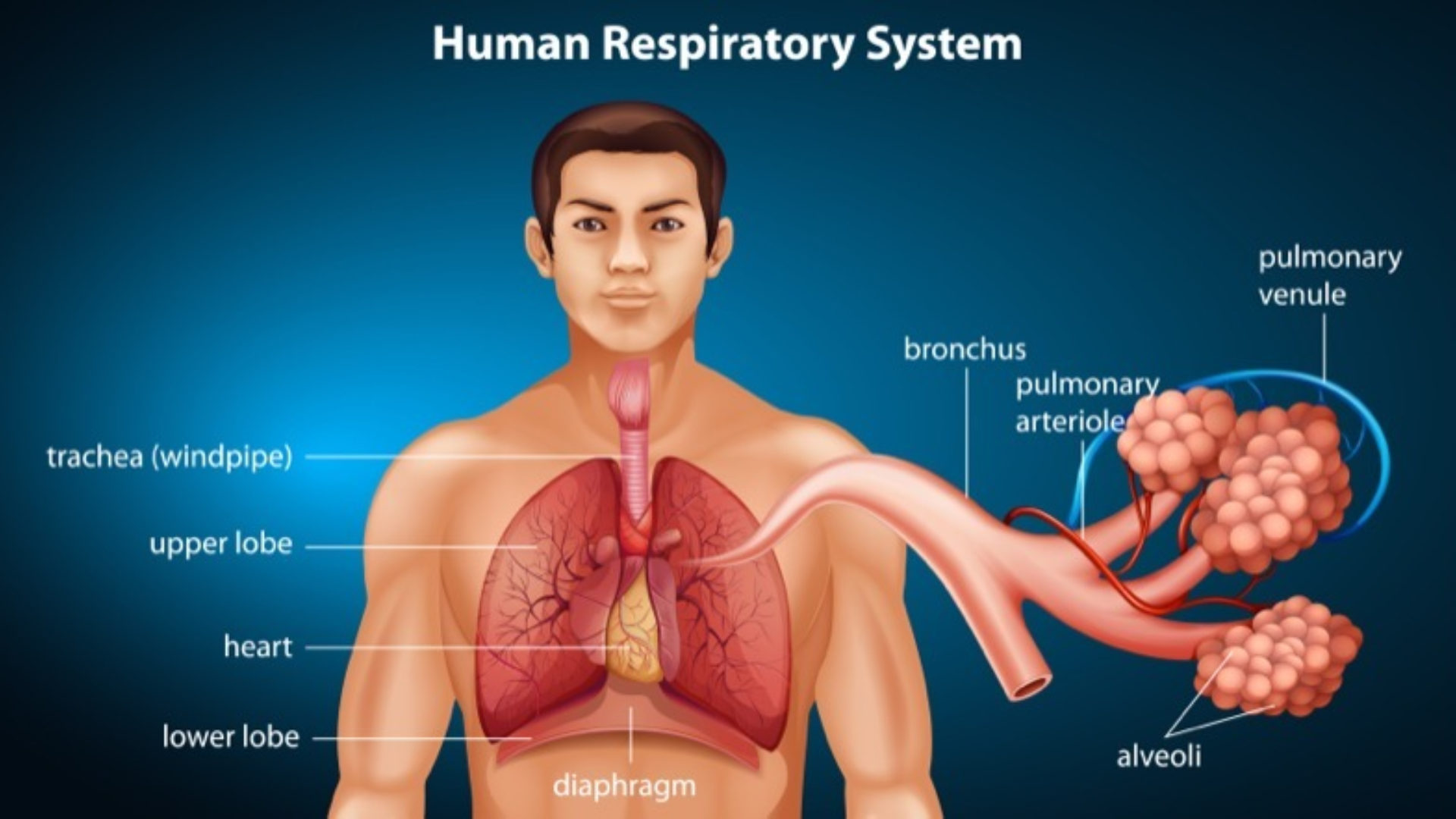
Anatomical dead space is the volume of air contained within the conductive airways of the respiratory system. Closing capacity is increased. This in a normal respiratory system consists of the nose pharynxlarynxtrachea bronchibland bronchioles.
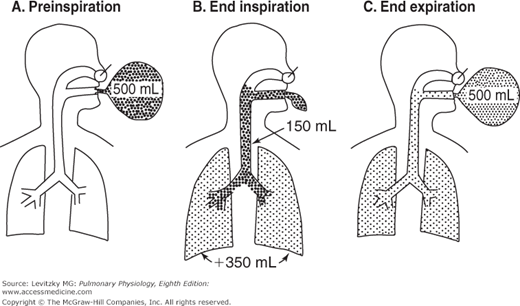
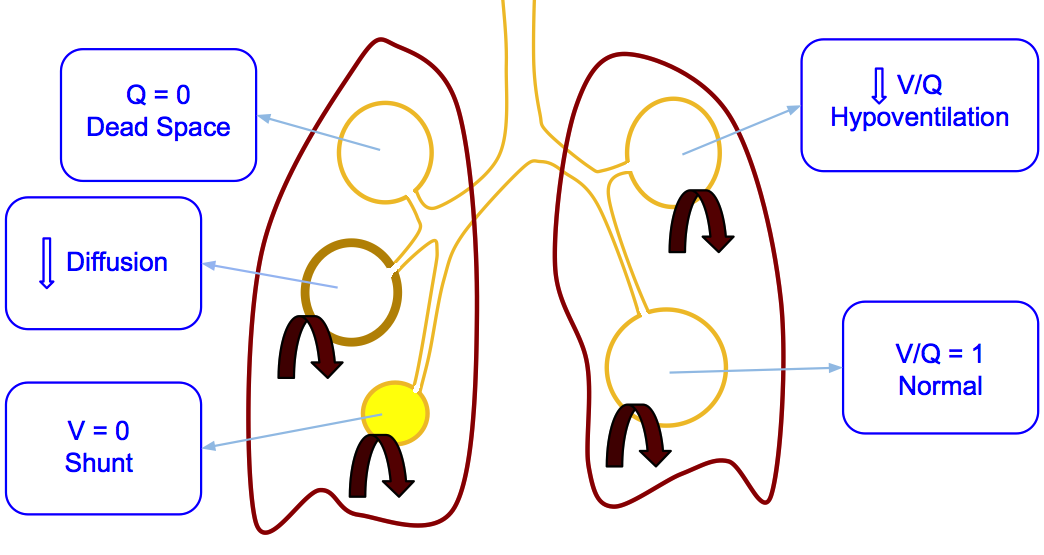
Bohr dead space Because of the tidal nature of ventilation every exhaled breath contains a fraction of the inspired gas that does not participate in gas exchange. Lung volumes and spirometry variables. Dead space is defined as an area with ventilation but no perfusion.
This limits the dead space to between the. Dead space Volume of the airways and lungs that does not participate in gas exchange Anatomical dead space Volume of conducting airways Upper airways larynx trachea bronchi and bronchioles Does not include respiratory bronchioles and alveoli Physiologic dead space VDphys. Dead space of the respiratory system refers to the space in which oxygen O2 and carbon dioxide CO2 gasses are not exchanged across the alveolar membrane in the respiratory tract.
Subscribe to the drbeen Channel HERE. It is composed of apparatus dead space and physiological dead space.
It is ventilation without perfusion.
Dead space is defined as an area with ventilation but no perfusion. The two types of dead space are anatomical dead space and physiologic dead space. Lung volumes and spirometry variables. Closing capacity is increased. Respiratory resistance is increased at birth. Medical Definition of dead space. Subscribe to the drbeen Channel HERE. Dead space Volume of the airways and lungs that does not participate in gas exchange Anatomical dead space Volume of conducting airways Upper airways larynx trachea bronchi and bronchioles Does not include respiratory bronchioles and alveoli Physiologic dead space VDphys. Start studying Chapter 13 Respiratory system.
It is composed of apparatus dead space and physiological dead space. Dead space is the volume of a breath that does not participate in gas exchange. The dead space in that portion of the respiratory system which is external to the alveoli and includes the air-conveying ducts from the nostrils to the terminal bronchioles compare physiological dead space. It can increase the total dead space. The normal ratio of dead space to tidal volume is in the range 02 to 035 during breathing at rest. The total dead space also known as physiological dead space is the sum of the anatomical dead space plus the alveolar dead. Httpbitly2GB41bUWatch drbeen videos HERE.































Post a Comment for "Dead Space In Respiratory System"